Startups need not only to create a product but also to showcase it to the market. Even a strong team and a good idea won't work if nobody knows about the project. One of the most accessible ways to attract an audience is through SEO. In this article, we'll explain what SEO is and provide SEO tips for startups.

Why SEO is Important for Startups
SEO for start ups is not just a trendy term but a viable tool that can significantly boost the growth of a new business. Search engine optimization startup helps solve several key tasks:
- Traffic Attraction. People use search engines. If your site doesn't appear in the results, you lose potential customers. Promoting your startup in Google allows you to secure a top spot and attract interested users.
- Building Trust. Users perceive a site found through search as a more reliable source.
- Reducing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC). In the long run, SEO for a startup business is cheaper than paid advertising.
Common Myths About SEO
Myth 1. The Key is to Be at the Top
Many believe that the success of SEO for a startup is reaching the top position in search engines. However, being at the top alone doesn't offer any benefits. What's important is the relevance of the queries for which the site appears there. If the query is irrelevant or not searched for, there will simply be no traffic. Effective SEO for startup business begins with understanding what users are searching for and how it relates to your product.
Myth 2. SEO is Slow and Expensive
Whether it's SEO for IT startups or SEO for tech startups, large investments aren't always necessary. Initially, it's enough to tidy up the website, fix technical errors, and publish useful content. Even such simple steps can lead to initial results. Yes, you shouldn't expect rapid growth. But don't delay with SEO – the sooner you start, the faster you'll see effects.
Myth 3. Keyword Stuffing Still Works
Search engine algorithms have long been able to understand the meaning of text. They consider synonyms, structure, user behavior, and content quality. Today, content for start up SEO must be useful and written for people, not just for robots. Over-optimization and keyword stuffing work against you. By following a start up SEO guide, you can focus on creating valuable content that resonates with your audience.
Myth 4. More Links – Better Results
In the past, the “more is better” approach was effective, but now link building for startups requires caution. The quality of links, relevance of donors, natural placement, and a well-thought-out anchor list are crucial. Bulk purchasing of links or spamming can not only be ineffective but also lead to penalties.
Myth 5. Meta Tags are the Basis of SEO
Yes, meta tags (title, description) are an important element of a startup's site optimization. But they are just one part of the system. Without quality content, internal optimization, a good structure, and a well-designed startup SEO guide, the site won't rank well. It should be viewed as one of the steps in a step-by-step SEO for startups, not as a universal solution.
Myth 6. Behavioral Factors Can be Manipulated
Attempts to artificially manipulate behavioral factors (clicks, transitions, time on site) are outdated. Google and other search engines can easily distinguish real actions from manipulations. Such methods are risky and, at best, ineffective, while at worst, they can lead to filters and loss of traffic.
Why It's Important for Startups to Start with SEO Right Away
In the early stages, a startup often lacks something: money, time, recognition. This is normal because resources are limited and tasks are numerous. But there's good news: SEO can address several important issues at once. While SEO isn't a magic solution or an abstract “investment in the future,” when properly implemented, it becomes a strategic asset working for you 24/7—even at night, when the ads are off, or you're in meetings or on vacation.
Advantages: ROI, Lower CAC, Strategic Edge
Affordable SEO for start ups is an investment that can yield significantly more than paid traffic. Results may not be immediate, but after a few months of a well-executed SEO strategy for startups, your site begins generating leads and sales without additional costs for each click.
CAC (customer acquisition cost) through SEO decreases over time: you don't pay for every visit—you invest in smart website architecture, SEO content for startups, and links (link building for startups).
And remember the strategic advantage: if you occupy a niche in search before your competitors, displacing you will be expensive and difficult.
Organic Traffic and Brand Awareness
People tend to trust websites that rank at the top. If your project frequently appears for key queries, you gain not only clicks but also attention, recognition, and reputation.
Comparison: SEO vs Paid Advertising
Paid advertising works like renting. As long as you pay, it delivers results. Stop paying, and it's gone. SEO works differently – you build a foundation that will yield results over a long time.
With the same budget, the initial effect of advertising is higher, but after a few months, SEO will start to catch up and surpass. This is especially noticeable in B2B and SaaS segments, where sales do not occur from the first interaction, and a user may return to the site 3-4 times through search engines.
For a startup, it is important not just to “get traffic” but to build a client acquisition system that works autonomously. How to set up SEO for a startup is a question that should be answered as early as possible.
How SEO Works for the Future: The Compounding Effect
SEO scales well. You don't need to restart a campaign each time. Content you create today will attract customers even a year from now. If you invest in SEO services for startups, including link building for startups, growth will accelerate significantly.
If you're just launching a startup, don't wait for a “budget.” A step-by-step startup SEO guide is foundational. Begin with technical site optimization, understand key queries, and launch your first articles. In six months, you'll thank yourself.
Is Your Startup Ready for SEO?
SEO is a powerful tool that works best when implemented at the right time. Start too early – you'll waste resources; too late – you'll miss the market. Therefore, when considering search engine optimization for start ups, the first question should be: are we ready for SEO? SEO for a startup company should begin with analysis.
Readiness Checklist
For SEO consultants for startups to be genuinely beneficial, several key conditions must be met:
- Product Market Fit
You clearly understand who needs your product, and there is already confirmed demand. - Understanding the Target Audience and Their Pain Points
Who is your customer? What annoys them, what do they search for on Google, and what terms do they use? Without answers to these questions, you can't create effective content for SEO for startups or choose relevant keywords.

- Resources: People, Time, Budget
SEO is not a one-time setup; it's a process. If you plan to handle SEO yourself, you'll need specialists (copywriter, analyst, developer), time to implement changes, and funds for content and links.
- Technical Foundation
The website should have a minimally SEO-compatible structure: a proper CMS, clean code, indexability, and a mobile version. Without these, any articles and keywords simply won't reach the user.
How Google Works and Its Impact on Business
To build a sound SEO strategy, it's important to understand the logic of search. Google doesn't “guess” what to show the user – it follows a clear system: Crawling → Indexing → Ranking.
- Crawling:
The search bot (Googlebot) navigates web pages to find new content. If your site is technically inaccessible or pages are hidden from indexing, you simply won't be found.
- Indexing:
After crawling, Google analyzes the page: content, structure, meta tags, headings, and more. Only indexed pages can participate in search results. Duplicates, junk pages, or markup errors hinder indexing.
- Ranking:
When a user enters a query, Google selects from indexed pages those that best match their expectations. Hundreds of factors are considered, from content to site reputation.
In simple terms: if your site isn't readable by the bot, isn't indexed correctly, or doesn't provide value to users, it won't appear in search results, no matter how hard you try.
E-E-A-T Principles: Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust
Ensuring your site is optimized for SEO is crucial for growth. Whether you're focusing on SEO for startups or seeking an SEO agency for startups, understanding these fundamentals is essential.
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is a content quality assessment system. It is particularly important for topics related to health, finance, safety, etc. (the so-called YMYL areas: Your Money or Your Life).
- Experience: The author has firsthand experience with the topic they are writing about (for example, a product manager discussing SaaS launch).
- Expertise: Content is written with a clear understanding of the subject, avoiding superficial generalizations.
- Authoritativeness: Other sources cite the website or author as an authoritative figure in the niche.
- Trustworthiness: Reliability of the site: presence of contact details, privacy policy, HTTPS, transparency.
For startups, this is especially crucial: if content appears like forum chatter and the author lacks expertise, Google will not promote such a site.
Impact of UX and Loading Speed on SEO
UX directly influences bounce rate, depth of visit, and time on site, all of which are signals for search engines.
For more insights, explore topics like link building for startups and SEO services for startups to enhance your strategy.
- Loading speed: If a site loads slowly, users leave, and Google lowers its search ranking. This is especially important for mobile traffic.
- UX factors: Easy navigation, readable text, and lack of annoying elements (pop-ups, auto-play videos) all impact behavioral signals.
Mobile-first indexing
Since 2019, Google uses mobile-first indexing . This means the mobile version of a site is prioritized in ranking.
This means that:
- If the mobile version is cut down or just for show, the site may not appear in search results.
- Content, links, and structure should be equally accessible on both mobile and desktop versions.
- Responsive design is now essential.
SEO Basics
If you're looking to grow your startup, focusing on search engine optimization for startups is key. For effective results, consider hiring a specialized seo agency for startups or a startup seo consultant.
- Keyword research
Keywords are what people enter into a search engine to find solutions to their problems. Your task is to understand which phrases potential customers use and how they formulate their queries at different stages of the funnel.
Types of Keywords and Goals
- Informational – “how SaaS CRM works,” “Zoom alternative,” “what is API.” The person is seeking knowledge, not a product.
- Transactional – “buy CRM for small business,” “cloud telephony prices.” Here, the user already has the necessary information and is ready to act.
Long-tail Keywords
These are more specific, low-frequency queries like “best CRM for a 5-person IT startup.” They are less commonly entered but have higher conversion rates because they more accurately reflect real demand. These keywords are particularly useful for new projects because it's easier to reach the top for them.
Tools
- Google Keyword Planner – a basic but free tool. Good for starters.
- Ahrefs , Semrush – tools that offer more functionality: frequency, competition, history of requests, related keywords. For example, Ahrefs Free Keywords Generator helps generate keyword ideas for specific services – Google, Bing, Amazon, or YouTube.
- Answer the Public , AlsoAsked – help find questions users ask.
Localization of Keywords
If your startup is targeting an international audience, it's crucial not just to translate keywords but to adapt them to the specific market. In the USA and Germany, queries will differ even for the same product. Here, local keyword research is helpful, preferably with the participation of a native speaker or local SEO specialist.
- Content Strategy
When you understand what users are searching for, it's time to build a content strategy.
Approach: Pillar Content and Clusters
- Pillar Page – a large article on a broad topic, for example: “How to Work in Figma: Complete SEO Guide for Startups.”
- Cluster Articles – materials on narrow subtopics: “How to Choose SEO Tools,” “Content Strategy for IT Startups.”
Articles are interlinked with internal links. This helps users navigate the site better and strengthens the structure from a search engine perspective.
Types of Content
- Educational : articles, step-by-step guides
- Practical : cases, instructions, checklists
- Image-building : research, white papers, expert opinions
A good content SEO strategy for startups includes all types.
Content for Different Funnel Stages (TOFU / MOFU / BOFU)
- TOFU (Top of the Funnel): informational materials answering basic questions.
- MOFU: comparisons, reviews, cases – content that helps in making a choice.
- BOFU: offer pages, FAQs, demos – things that help in decision-making.
SEO Content vs. Branded Content vs. “Viral” Content
- SEO Content – written for demand and works for traffic.
- Branded Content – shapes the image, tells about you.
- “Viral” Content – interesting, engaging, but not always search-oriented.
It's vital not to focus on one approach but to combine them. A startup needs traffic, trust, and recognition.
- On-page SEO
This involves working with the content on the page: structure, tags, content, links. It determines whether Google understands what your page is about and how well it meets user queries.
Headings (H1–H3), Meta Tags, Alt Texts
- H1 – Page Title. One per page. Should be specific and include the key query.
- H2–H3 – Subheadings. Divide the text into sections and help bots (and people) navigate.
- Title and Description. Meta tags visible to the user in search. Title is important for ranking, while description affects CTR.
- Alt Texts. Text descriptions of images. Needed for accessibility and provide additional SEO signals, especially in thematic articles.
Internal Linking and URL Structure
- Linking helps distribute weight between pages and simplifies navigation. For example: in an article about SEO, you can link to an article about Keyword Research and vice versa.
- Human-Readable URLs: site.com/blog/seo-for-startups, not site.com/page?id=123. Short, concise addresses are a big plus for ranking.
Structured Data, FAQ Schema
Using Schema.org , you can mark up content so that the search engine understands its structure: prices, ratings, FAQs.
Especially useful:
- FAQ Schema – questions and answers right in the snippet.
- Article Schema – for blogs and guides.
- Product Schema – for product cards or SaaS plans.
Improving CTR in Search Results (Rich Snippets)
CTR (click-through rate) is the percentage of clicks your result gets in search results. Even if you're third, a well-crafted snippet can “steal” attention.
- Use clear, attractive titles.
- Add numbers, specifics, call-to-action in the description.
- Use proper markup.
- Technical SEO
Technical SEO is everything that helps search engines crawl and display your site properly for users. You can create a great content strategy and write excellent articles, but if the site is poorly configured, Google still won't see you.
Mobile Adaptation, HTTPS, and Speed (Core Web Vitals)
1. Mobile Adaptation
Google has long switched to mobile-first indexing – it looks at the mobile version of the site first. Regularly check your site via the Mobile-Friendly Test .
2. HTTPS (SSL Certificate)
Without HTTPS, browsers may mark the site as “unreliable.” This affects not only user trust but also SEO. Install a free certificate (e.g., Let's Encrypt).
3. Loading Speed and Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are three metrics that assess how fast and conveniently a site loads:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): how long it takes for the main block of the page to load.
- FID / INP: how quickly the site responds to actions (clicks, scrolls).
- CLS: whether the layout jumps during loading.
Google considers these metrics important for UX and therefore for ranking.
You can check your site with Lighthouse .
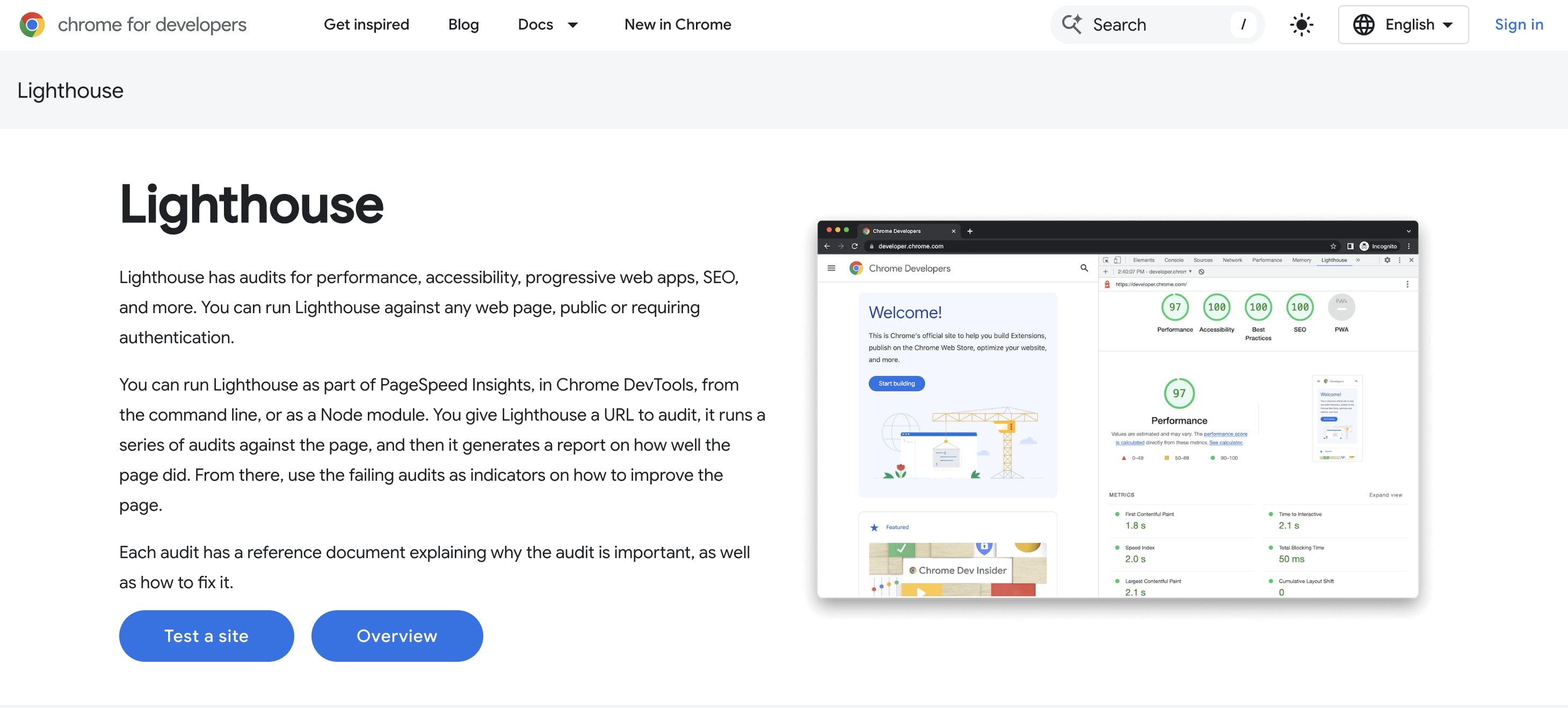
Sitemap.xml, robots.txt, canonical, 404/301
These tools manage what Google sees and how it processes it.
Sitemap.xml
This is a list of all important site pages. It helps the search engine find and index the necessary sections faster. Especially useful for new sites with few external links.
robots.txt
A file that tells search bots: “this can be crawled, but not this.” For example, you can close the cart, filter pages, duplicates. Errors in robots.txt can lead to complete site invisibility in Google.
Canonical
If the same page is accessible via multiple addresses (e.g., with and without a trailing slash), the search engine may consider them duplicates. Canonical shows which version to consider primary. This helps avoid splitting the ranking among copies.
301 and 404
- 301 (permanent redirect): tells the search engine and browser that the page has moved. Preserves SEO weight.
- 404: page not found. This page should be well-designed, with an option to return to the main page or search. Poorly configured 404 pages signal Google to a “bad” site.
Indexability Check
Sometimes a page exists with a lot of useful content, but traffic is zero.
Possible reasons include:
- The page is blocked from the search engine in robots.txt,
- A noindex meta-tag is in place,
- Poor internal link structure,
Periodically, audits should be conducted: manually or via tools.
What to Check Why Tools Mobility Mobile-first index, UX Mobile-Friendly Test, GSC Loading Speed and Stability Behavioral factors and ranking PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse HTTPS Trust, security, SEO factor Browser / SSL checker Page Indexability So the content is visible in search Google Search Console, Screaming Frog Sitemap and robots.txt Crawling management Manual check, GSC Canonical and redirects Combating duplicates, saving weight Ahrefs Site Audit, SEO Spider
- Off-page and Link Building
Off-page SEO refers to actions beyond the website itself that influence rankings. This includes inbound links. Google still views a link as a signal of trust – if you are being linked to, your content deserves attention.
But not just any “mass,” the quality and context of links are important. Especially for a startup, where you're building not only SEO but also a reputation.
Types of Links: Dofollow, Nofollow, UGC
- Dofollow – a “full” link that transfers SEO weight (PageRank). This is the backbone of link building.
- Nofollow – the search engine considers such a link but does not transfer the weight directly. Used for advertising, user-generated, and unreliable links.
- UGC (User Generated Content) – links from comments, forums, etc. Marked as user-generated content. Usually ignored but can be useful for diversifying the link profile.
Important: Chasing numbers makes no sense. Ten quality dofollow links are better than 200 suspicious nofollow ones from spam directories.
Methods of Acquiring Links
- Guest Posting
Write an article for a blog or media in your field in exchange for a link. The main thing is not to advertise but to share experience.
- Digital PR
Promotion through news: announcements, investments, partnerships, research. Provides not only links but also mentions in authoritative media. Works for SEO and recognition.
- HARO / Help a Reporter
Services where journalists seek experts for comments. If you're cited, you get a link from media, often with high authority (DR/DA).
- Directories and Business Platforms
Relevant for SaaS, local services, and B2B. Examples: Product Hunt, Clutch, G2, Capterra. The main thing is not to use spam directories but to list where you can actually be found.
Reputation Factor (Unlinked Mentions)
Google considers not only links but also mentions of the brand without an active link . This is called implied links . Mentions in media, blogs, and forums strengthen site credibility.
Tools for Link Analysis
To build and track the link profile, tools are needed. They show:
- Where links are coming from,
- Which ones are live / dofollow,
- The donor's “weight,”
- Anchor text,
- Growth or loss trends.
Tool Main Features Price in 2025 Suitable for Ahrefs Link analysis, anchor list, competitors, growth from €119/month Deep analysis + content plan Semrush Backlinks, site audit, outreach, competitors from $117/month Marketing + SEO Moz Domain Authority, link analysis, spam filters from $49/month Basic SEO optimization, position tracking, and site error control Majestic Trust Flow / Citation Flow, visualization from €46.99/month In-depth link mass analysis
Step-by-Step SEO Guide for Startups
- Define Goals and Audience
Before purchasing articles, setting up meta tags, and hiring contractors, ask yourself a simple yet essential question: why do you need SEO?
Do you want to:
- Attract traffic from search engines?
- Gather leads and sales?
- Increase product awareness?
- Establish a position in an expert niche?
The goal determines the approach. For example:
- If you need quick leads , focus on BOFU content and commercial pages.
- If you're building an expert brand , concentrate on articles, guides, and reputation links.
- If you're in a competitive niche, you'll need a long-term link building strategy and technical enhancement.
Next, identify your target audience:
- Who are these people?
- What are they searching for?
- How do they phrase their inquiries?
- At which stage of the funnel are they searching?
Your semantics and content will be built around answers to these questions. Without this, SEO is just randomly placing keywords.
- Use the SEO Promotion Calculator from LinkBuilder.com
To avoid building a strategy blindly, start by analyzing competitors.
SEO Promotion Calculator is a free tool that helps you understand link building costs based on competitors' real backlink data.
How it works:
- Export competitors' backlinks from Ahrefs, Semrush, or other SEO tools.
- Upload the file (CSV or TXT) to the calculator.
- Receive a cost estimate and link composition: by type, DR, platforms, etc.
Advantages:
- The service is free and requires no registration;
- Supports up to 5000 links;
- Allows you to understand the scale of link building and estimate costs.
By registering, you gain access to donor databases, additional analytics, and extended functionality.
This enables you to:
- Avoid unnecessary expenses;
- Compare competitors by backlink profile;
- Build a realistic SEO strategy.
Besides the SEO Promotion Calculator, you can use our Guest Post Selection Tool for these purposes.
By subscribing to the tool, you will receive:
- Access to a database for outreach and guest posts, as well as a database for free link posting, enhancing your link building strategy;
- All sites are checked for top SEO metrics;
- The tool's functionality is designed to make your work as convenient and effective as possible.
Read our guide How to Budget Link Building Using Competitor Analysis Strategies for more details.
- Select Keywords
Keywords are the foundation of all SEO work. Without them, you're “pushing” content into a void. To understand what your potential clients are searching for, you need a simple yet accurate semantic core.
What to do:
- Use Google Keyword Planner , Ahrefs , Semrush , depending on your budget.
- Gather all query variations related to your product, customer problems, and niche.
- Divide keywords into commercial (like “buy cloud CRM”) and informational (“what is CRM”, “how to choose CRM for small business”).
- Pay attention to frequency and intent . It's important not only how often a query is searched each month but also why.
Without keywords, content may not meet audience needs, and commercial pages won't rank well if written on a whim.
- Optimize the Website
You're probably wondering how to promote a startup in search engines. Now that you know which queries to target, it's time to organize your site.
Key actions:
- Check the technical base : responsiveness, HTTPS, load speed, correct indexing.
- Set up a logical URL structure .
- Add meta tags (Title, Description) to all important pages.
- Ensure each page has a unique H1 , logical subheading structure (H2, H3), and alt texts for images.
- Set up sitemap.xml and robots.txt .
Without technical optimization, even perfect articles and well-planned semantics may fail because the site won't index properly, might load slowly or duplicate, leading Google to skip it.
- Create Quality Content
Considerations:
- Write articles, guides, descriptions, and case studies for specific queries and funnel stages.
- Use keywords naturally, don't overstuff.
- Structure content well.
- End articles with a call to action, especially if it's BOFU content.
Google evaluates not just keywords but also user behavior: do they keep reading, click further, or linger on the site?
- Build External SEO for the Startup (Links)
Links to your site are key for Google to determine trustworthiness. Like recommendations, the more authoritative resources mention you, the higher your chances to reach the top.
Initial steps:
- Obtain links from forums , niche-specific Telegram channels, Reddit, Quora, Dev.to, Stack Overflow (if relevant).
- Write guest articles for niche blogs or media.
- Conduct outreach : contact site owners for mutually beneficial cooperation.
- Publish in directories .
- Set Up Analytics
In SEO, everything must be measured: traffic, positions, user behavior. Without data analysis, you won't know what's working.
Initial setup:
- Google Analytics – for tracking traffic, behavior, conversions.
- Google Search Console – for analyzing search queries, indexing issues, clicks, and positions.
- Yandex.Metrica – if targeting a Russian-speaking audience.
Additionally:
- Ahrefs / SEMrush / Serpstat – for tracking link growth and keyword positions.
- Hotjar, Clarity – for session recordings and heatmaps (behavioral analysis).
Why it's needed:
To understand which articles drive traffic, why users leave certain pages, etc. Without this, SEO is just guesswork.
- Improve and Update
Google favors live sites, not archives:
- Update content , especially informational articles. Add fresh data, examples, and improve structure.
- Remove or merge weak pages that don't get traffic or provide value.
- Test titles , CTAs, page structure. Even small changes can significantly influence user behavior.
- Monitor positions and adapt strategy: find reasons for drops, scale successful approaches.
Google constantly re-evaluates content. What ranks today might drop tomorrow if quality isn't maintained.
SEO at Different Stages of a Startup
- Pre-launch (Before Launch)
Objective at this stage: Lay the groundwork and start building an initial audience.
What to do:
- Create a simple landing page (waitlist, early access) with SEO-friendly elements.
- Begin gathering keywords to understand what your target audience is searching for.
- Prepare the future site's structure with SEO in mind.
- Set up basic analytics (Google Analytics, Search Console).
- Set up email collection through forms or lead magnets (e.g., PDF/guide).
- MVP and Early Launch
Objective at this stage: Test hypotheses, gain initial traffic, understand what works.
What to do:
- Create initial pages for key queries (e.g., a blog with 3–5 articles).
- Optimize the structure and headers of the pages.
- Start testing behavioral factors (on-site behavior, CTA).
- Conduct a quick SEO audit: indexability, canonical URLs, site speed.
- Begin building initial links (listings in directories, niche media).
- Growth and Scaling
Objective at this stage: Build a stable organic channel and scale content.
What to do:
- Develop a content strategy: topic clusters, publish pillar content.
- Consistently publish articles, guides, case studies.
- Launch link building campaigns: guest posting, PR, HARO, community outreach.
- Conduct a technical audit and fix accumulated issues.
- Deepen analytics: track not just traffic but also conversions and user behavior.
- Automate processes (content planning, SEO reporting).
- Scale: Strengthening and Long-term Strategy
Objective at this stage: Dominate search within your niche. Search engine optimization for start ups is essential at this step.
What to do:
- Target competitive keywords.
- Enhance brand authority (E-E-A-T).
- Expand content: video, infographics, research.
- Implement a process for continuous content updates.
- Expand presence in SERP: FAQ blocks, featured snippets, local SEO if applicable.
How to do SEO Cheaply and Effectively
When resources are limited, it's crucial to spend them wisely, especially in the early stages.
What You Can Do Yourself
- Basic technical optimization of a startup's website (using guides)
- Content: Maintain a founder-led blog or publish expert articles.
- Manual keyword research and clustering (using free/cheap tools)
Risks of Cheap SEO
- Automatic link generation (spam, Google penalties)
- Template-based, non-unique content
- Promises of “guaranteed rankings” – a clear marker of black-hat practices
- Lack of transparency in reporting
How to Choose an SEO Agency
Choosing a contractor is a crucial step, especially if you lack in-house expertise. Here's how to approach it wisely.

Signs of a Good and Bad Contractor
| Bad Contractor | Good Contractor |
|---|---|
| Promises “TOP-1 in a month” | Provides honest timelines and limitations |
| Doesn't inquire about the product/business | Delves into goals and target audience |
| Uses template strategies | Tailors to your stage and niche |
| No transparent reporting | Offers clear reports with analysis |
When considering SEO services for startups, it's important to work with a reliable startup SEO consultant to ensure effective link building for SEO startups.
Questions to Ask an Agency Before Starting Work
- Do you have experience working with startups?
- How do you approach strategy development, where will you start?
- What KPIs and metrics do you track (traffic, rankings, leads, conversions)?
- How often do you provide reports? What do they include?
- Can you show examples of similar case studies?
Important: A good partner will ask counter-questions about the product, target audience, and business goals, indicating a systematic approach.
About KPIs and Reporting
At the beginning, it's crucial to agree on what will be considered a result. For example:
- Increasing the number of organic leads.
- Improving rankings for key queries relevant to your product.
- Acquiring links from authoritative resources.
- Enhancing technical metrics: speed, indexability, absence of duplicates.
Who to Trust with Startup SEO?
When you need not just a contractor but a strategic partner capable of ensuring quality growth even with limited startup resources, LinkBuilder.com is an excellent choice.
This approach to SEO for tech startups and seo for growth can be crucial for your business success.
- Comprehensive link building – from manual submissions and forum links to niche edits , promotion via HARO and Digital PR (including media outlets)
- Extensive and verified donor database – over 220,000 sites, with flexible filters, DR/DA metrics, countries, and pricing
- Comprehensive solutions for startups – you can order a one-time service or launch a turnkey strategy with flexible rates and scalability.
Integration of SEO with Other Channels
How SEO enhances email marketing and social media
Content created for search queries works excellently with other channels:
- Email Marketing : SEO content helps expand the touchpoint chain. For example, a guide on “How to Choose CRM for a Startup” can be:
- Used as helpful material in a welcome email series,
- Included in a newsletter labeled “best from the blog”,
- Broken into a series of short emails.
- Social Media : Articles created for search traffic provide reasons for native posting. Especially effective are:
- Carousels based on lists from the article,
- Quotes and “how-to” formats,
- Discussions around the pain points addressed by the SEO content.
SEO as a Foundation for Targeting and Remarketing
Content created for SEO can be used more effectively in paid channels than abstract landing pages:
- For Remarketing : If someone has already read an article on the blog, you can show them a relevant offer or lead magnet through social media ads.
- For Targeting : Topics that people search for (and for which you already rank) can be turned into segments for Lookalike or interests.
Additionally, SEO acts as a demand research tool and helps target advertising more accurately to address specific pain points.
Content Reuse: One Text – Multiple Channels
If you've invested resources in quality SEO content, don't limit yourself to one channel. A well-structured guide can be turned into:
- A thread on X / LinkedIn (e.g., top 5 insights)
- A video or webinar (based on chapters from the article)
- A series of stories or short clips
- A PDF lead magnet or mini-book
This approach not only saves resources but also enhances a multichannel funnel: the same message reaches the user in different formats and touchpoints.
Using AI and Automation in SEO
At the start, when the team is still small, AI can be a good accelerator. However, it's crucial to use artificial intelligence correctly to maintain quality and avoid penalties from search engines.
Where AI Really Helps: From Drafts to Clustering
AI tools won't replace your SEO specialist, but they can effectively handle specific tasks:
- Drafting article outlines
- Generating titles, meta descriptions, alt tags. Especially useful for a large number of pages (e.g., catalogs).
- Keyword grouping (clustering). With AI, you can speed up semantic markup.
- Content and structure ideas. AI helps identify topics you might have missed.
Example: ChatGPT can provide 10 guide ideas for your niche, then assist in outlining subheadings, including SEO elements (h1–h3, tables, FAQs).
Popular tools: AI Ranker, ChatGPT, Jasper, SurferSEO, NeuronWriter
Each of these tools serves a specific purpose:
- AI Ranker – free AI analysis of website visibility in search: frequency of mentions, citations, improvement recommendations.
If you're looking at optimizing your search engine visibility, tools like these can be part of a startup SEO guide, offering valuable insights and strategies.
- ChatGPT is versatile: ideas, structure, reframing, answering questions.
- Jasper.ai specializes in copywriting, suitable for landing pages, emails, and promotional texts.
- SurferSEO suggests which words to use in the text to align with top SERP results.
- NeuronWriter is an alternative to Surfer. Helps improve semantic coverage and E-E-A-T approach.
How to Avoid Google Penalties for AI Content
The main question: Can AI be used in content without harming the site? Yes, it can, but with conditions:
- Google is not against AI if the content is useful and written for people.
- Risks arise when:
- The text is generated without editing and meaningful value,
- Pages are created en masse just for keywords (“AI-filled catalogs”),
- E-E-A-T principles are violated (lack of sources, expertise, authorship).
Consider leveraging SEO for startup busines to ensure your AI-driven content remains effective and compliant.
To avoid issues:
- Always edit and review AI-generated texts,
- Add unique examples, case studies, visuals,
- Maintain a balance between automation and real user value.
SEO for International and Multilingual Startups
Entering the international market not only opens new opportunities but also adds SEO challenges. Simply translating a website is not enough. It's important to understand how search works in each country, what phrases users employ, and how to properly structure a site for multiple languages and regions.
Hreflang, Subdomains, or Subdirectories: How to Structure a Multilingual Site
The first question to address is how to technically organize different language versions of the site.
- Hreflang tags help Google understand which page is intended for each region. For example, en-us for the USA and en-gb for the UK. This prevents content duplication and ensures the correct version is displayed to users in search results.
- Subdomains (fr.site.com, de.site.com) are suitable if you promote each version of the site as a separate project. They are often used by large SaaS or e-commerce platforms.
- Subfolders (site.com/fr/, site.com/de/) are usually the optimal choice for startups. It's easier to manage such a site, and all SEO weight remains within one domain.
Localizing Not Just Text, But Keywords
Simple translation doesn't work because people use search engines differently in various countries:
- In Germany, people search for “cloud telefonanlage” instead of “cloud phone system.”
- In France, it's “logiciel CRM gratuit” instead of “free CRM software.”
Therefore, it's important to:
- Create separate keywords for each country and language.
- Use local phrasing if it differs from the “global” naming.
- Adapt not just articles, but also titles, meta descriptions, call-to-actions, navigation, and images.
If you are looking for effective strategies, consider exploring SEO for startups to understand the nuances of optimizing for different markets and ensuring your startup SEO is comprehensive and effective.

Adapting Strategy for Local Search Engines
If you are targeting more than just Google, it's important to consider the specifics of other systems:
- Bing (USA): more attention should be paid to technical quality, micro-markup, and local content.
- Baidu (China): Works differently, requires separate hosting in China and simplified pages.
- Naver (South Korea): Focus on content and aggregators, more challenging with direct SEO, needs content PR.
Even with Google, approaches can vary by region: in the US, SEO competition is higher, while in Spain or Latin America, there are fewer queries but more potential for informational content.
It's crucial to remember that SEO for a multilingual startup requires a distinct strategy: technical, semantic, and content-related.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Started Too Early or Too Late
The Problem:
- Some start when the product isn't ready yet, so the content floats aimlessly, fails to address issues, and loses relevance.
- Conversely, some companies launch SEO when the market is already saturated and competitors are established in search results.
How to avoid:
- The optimal time is after the first signs of product-market fit, when you understand the audience and demand but it's not too late to claim your niche.
- Remember, Pre-launch is ideal for preparation, MVP for content, and Growth for scaling.
No strategy, only tactics
The problem:
- Articles are written, meta tags are added, links are bought, but without a system. The result: scattered traffic and no growth.
How to avoid:
- Start with goals (do you want traffic, sales, reach?).
- Build a funnel – TOFU / MOFU / BOFU.
- Gather keywords, create a content map, allocate resources.
- First, an SEO strategy for a startup, then take action.
Ignoring UX and mobile version
The problem:
The site is inconvenient, overloaded, and loads slowly on mobile. Users leave, and Google lowers rankings.
How to avoid:
- Address user experience early with startup SEO guide insights.
- Ensure mobile optimization to retain users.
- Design for mobile devices.
- Speed up your site: compress images, remove unnecessary elements, and configure caching.
- Test key pages on real devices, not just in emulators.
Over-optimization and Keyword Stuffing
The problem:
- Keywords in every paragraph, spammy text, headlines like “CRM for CRM with CRM about CRM.” This worked in 2010, but not anymore.
How to avoid:
- Write for people, not algorithms.
- Mention keywords 1–2 times where it feels natural.
- Use synonyms, clarifications, and thematic terms.
“Dead Blog” Without Updates
The problem:
- A blog is launched, but only three articles are published. Or 2019 guides still labeled as “New Trend.”
How to avoid:
- Update materials at least every 6–12 months.
- Add case studies, numbers, and fresh links.
- Build a regular content plan – at least 1–2 articles per month.
Relying on Link Buying and “Black Hat” Methods
The problem:
- Purchased links from “spammy” sites, scripts for automatic link generation. This leads to rapid growth, but inevitably results in filters and traffic loss.
How to avoid:
- Focus on sustainable SEO strategies like “link building for startups” and avoid shortcuts that harm long-term growth.
- Consider working with a startup SEO consultant or an SEO agency for startups to ensure ethical practices.
- Invest in creating high-quality, relevant content that naturally attracts backlinks.
- Focus on quality: thematic websites, relevant articles, white-hat methods.
- If using paid placements, ensure you verify domains and avoid mass posting.
- Don't use “sitewide” links and avoid using the same anchors everywhere.
Mistakes in SEO can be costly: you'll lose not only time and money but also search engine trust. Work methodically and patiently, and SEO will indeed become an asset rather than a headache.
Roadmap SEO: First 30 / 60 / 90 Days
Here's a clear plan for the first three months working with a startup website. This approach will help you stay focused and see initial results by the third month.
0–30 Days: Diagnosis and Preparation
At this stage, you're not promoting anything yet. Your goal is to properly prepare the platform.
What to do:
- Conduct a website audit : speed, indexability, mobile version, structure.
- Define SEO goals : traffic, leads, brand awareness (depending on business objectives).
- Develop an audience profile and funnel .
- Gather semantics : keywords for funnel stages, commercial and informational.
- Fix technical errors (https, redirects, canonical, robots.txt, sitemap.xml).
Checkpoints:
- Structure and keywords are set.
- Technical foundation is solid (Core Web Vitals, indexing, mobile-friendliness).
- Analytics configured (GA, GSC).
30–60 days: content and link building launch
Start publishing content.
Tasks:
- Write and publish the first articles and landing pages (TOFU/MOFU).
- Launch a content funnel: at least 1–2 articles per week.
- Begin link building: directory placements, initial guest posts, HARO, forums.
- Monitor technical stability and site performance under load.
Checkpoints:
- Initial search traffic appears (even if minimal).
- Content is indexed and visible in Google Search Console.
- First inbound links appear (even if nofollow).
Link building for startups and effective SEO strategies are essential components in ensuring the growth and visibility of a new business.
60-90 Days: Analysis and Scaling
After 2 months, it's time to evaluate what works and what doesn't, and strengthen the best channels.
Actions:
- Analyze which articles generated traffic. Update and refine them.
- Add commercial BOFU pages: case studies, offers, FAQs.
- Scale the content plan: more topics, longer materials, new formats (videos, PDFs, checklists).
- Enhance link building: engage in outreach, digital PR, partnerships.
- Test headlines, snippets, CTAs, and improve internal linking.
Milestones:
- Movement in rankings (for main queries) is visible.
- Search traffic begins to grow.
- First organic leads or sign-ups appear.
- It's clear what works and what doesn't. You can plan a strategy for the next 6–12 months.
Key Metrics for Evaluation
- Organic Traffic (search channel)
- Keyword Rankings (especially commercial)
- Page Indexability (number of pages in index / in sitemap)
- User Behavior (bounce rates, time on page, depth)
- Conversions from SEO Channel (registration, inquiry, purchase)
Conclusion
SEO is a transparent and measurable channel for attracting traffic and leads. While it won't replace other tools, it gives you the opportunity to accumulate results and reduce dependence on paid advertising.

This article covers:
- Why it's important to start SEO at the right time.
- How Google search works and what affects site visibility.
- SEO components: working with keywords, content, pages, technical parameters, and links.
- Considerations for marketing on international markets.
- Common mistakes that hinder startups and how to avoid them.
If you need help developing a strategy or launching SEO for a startup, you can contact LinkBuilder.com . We will help you build a strategy, strengthen the foundation, and launch content and links.








