Google E-E-A-T is a set of principles that the search engine uses to evaluate the quality of content. This acronym stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
Understanding what is EEAT in SEO is crucial for success in search engine optimization. It helps create content that ranks better, builds trust with users and search engines, and ensures a website’s resilience to algorithm updates. In this article, you’ll learn how to create expert content for Google and how to audit your website for compliance with SEO EEAT principles.
What is Google E-E-A-T: A Comprehensive Breakdown
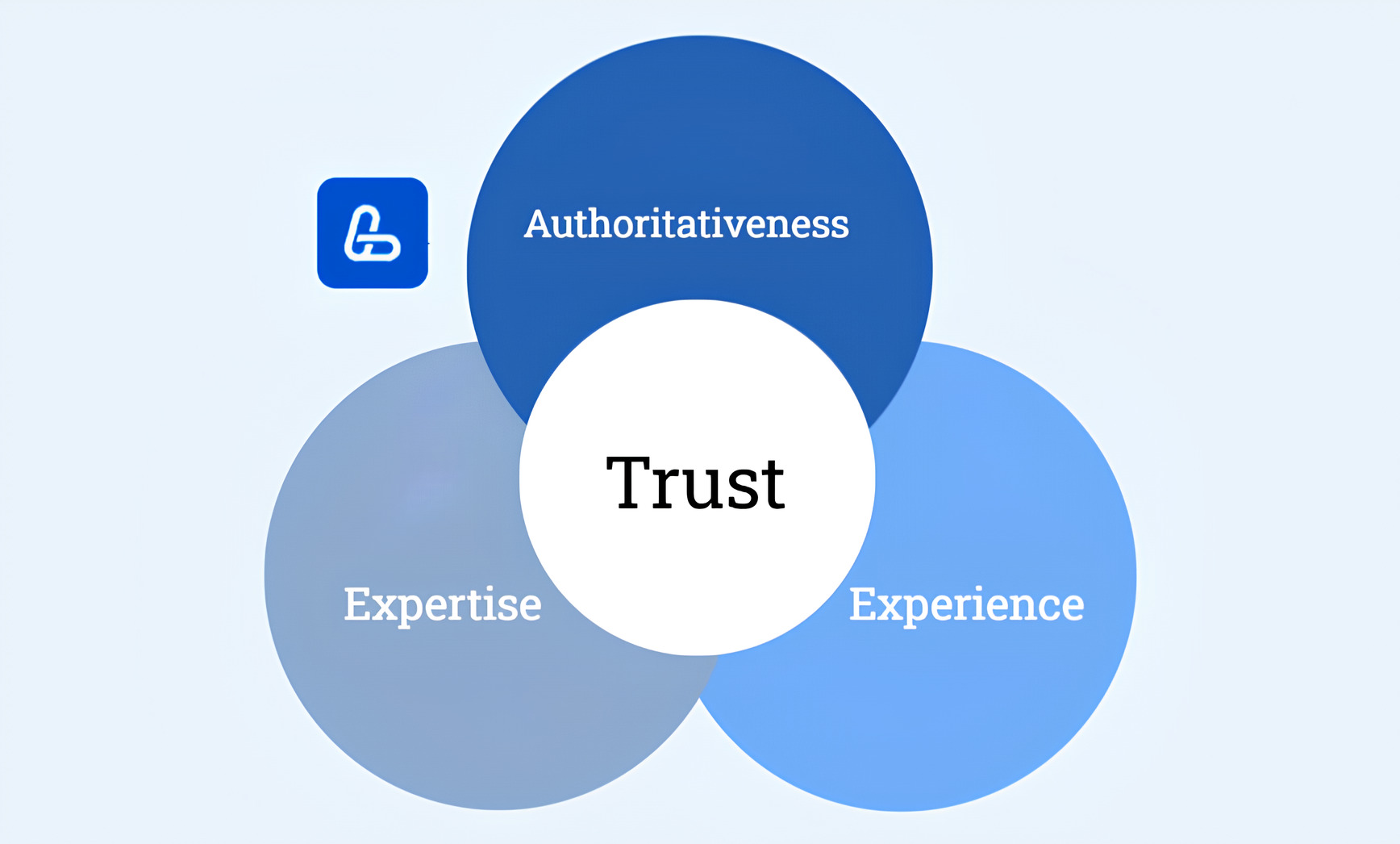
E-E-A-T is first mentioned in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines, a document for assessors who manually evaluate the quality of search results. While this document doesn’t outline direct ranking factors, it reflects Google content guidelines for what constitutes high-quality content. To better understand these principles, let’s dive into each component of what is Google EEAT in detail:
Experience: Demonstrating Firsthand Knowledge in Content
Experience evaluates whether the author has real-world interaction with the topic they’re writing about. Google values content rooted in personal experience. For example, a smartphone review from someone who has actually used the device will include more valuable details than a text based solely on a press release’s specifications.
Signs of experience in content:
- Unique observations not found in other sources
- Original photos and screenshots
- Practical tips from real-world use
- Descriptions of uncommon situations and their solutions
Expertise: What Google Considers Expert Knowledge
Expertise refers to a deep understanding of the topic. Google evaluates expertise differently depending on the subject matter.
For YMYL (Your Money Your Life) topics – finance, health, safety – formal expertise is required, such as relevant education, certifications, or professional experience. For non-YMYL topics (hobbies, lifestyle, entertainment), “everyday expertise” suffices – deep knowledge of the subject without formal qualifications.
Signs of expertise in content:
- Depth and detail in the material
- Accurate use of professional terminology
- Citations of studies and authoritative sources
- Information about the author’s professional credentials
Authoritativeness: Building a Reputation in Your Niche
Authoritativeness is the reputation of the author or website within their niche. Unlike expertise, which you claim yourself, authoritativeness is granted by others.
Signs of authoritativeness:
- Mentions and citations in other authoritative sources
- High-quality backlinks from relevant websites
- Recognition within the professional community
- Invitations to speak at industry events
- Endorsements from experts and thought leaders
Trustworthiness: Building Confidence in Your Content
Trustworthiness is about the reliability and truthfulness of the information. It’s the most critical criterion, often placed at the forefront in Google helpful content guidelines. Websites with high trustworthiness demonstrate a responsible approach to publishing content.
Signs of trustworthiness:
- Accurate and verified information
- Transparency about authors and website owners
- Clear distinction between facts and opinions
- Regular updates to outdated content
- Presence of a privacy policy and data handling practices
- Website security (HTTPS)
- Absence of misleading information
From E-A-T to E-E-A-T: Why Google Added “Experience”
In December 2022, Google updated its Quality Rater Guidelines, adding “Experience” to the existing E-A-T framework, which stands for expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. This change reflects the growing importance of firsthand experience in creating high-quality content.
Why Google introduced “Experience”:
- Combating artificial content. With the rise of AI, it’s easier to produce professional-sounding texts that lack real-world experience. Google aims to distinguish content from those who genuinely understand the topic.
- Demand for practical value. Content based on real expertise typically includes useful details and nuances that make it more helpful to users.
- Response to content marketing trends. Many companies create content on topics they lack experience in just to drive traffic. Google seeks to promote more authentic content in EEAT marketing.
- User expectations. People value advice from those with real-world experience, and Google accounts for this in its ranking algorithms.
What EEAT Meaning Implies for Search Engine Optimization
A common question is: Is Google E-E-A-T a ranking factor?
Technically, EAT in SEO is not a direct ranking factor. Google doesn’t have a single “EEAT score” that can be measured. Instead, these principles are implemented through various algorithmic signals:
- Quality and quantity of backlinks
- Brand mentions across the web
- Author signals
- Relevance and accuracy of information
- Technical aspects of the website
- User behavior metrics
Why E-E-A-T Is the Foundation of Quality Content
E-E-A-T has become the cornerstone of quality content for several reasons:
- Fighting misinformation. In an era of fake news, Google prioritizes content from reliable sources.
- Protecting users. For YMYL topics, inaccurate information can have serious consequences. E-E-A-T helps filter out potentially harmful content.
- Enhancing user experience. Content with high E-E-A-T typically better addresses user queries, providing more accurate and helpful information.
- Algorithmic updates. Many major Google updates (e.g., Core Updates) emphasize content quality and source authoritativeness.
- Long-term strategy. Unlike tactical SEO tricks, investing in EEAT signals ensures sustainable search rankings.
How Google Evaluates E-E-A-T: Algorithms and Criteria

E-E-A-T evaluation combines algorithms and manual reviews by assessors. While the exact mechanisms are Google’s trade secret, we can identify key EEAT signals considered.
Key E-E-A-T Signals for Search Engines
Google uses multiple signals to assess a website’s E-E-A-T:
- Backlink profile – number and quality of links from authoritative sites in your niche.
- Brand mentions – how often your brand is referenced online, even without direct links.
- Author signals – information about content creators, their qualifications, and external publications.
- Freshness and relevance – how frequently content is updated, especially for topics where information quickly becomes outdated.
- User signals – how people interact with content (time on page, bounce rate).
- Technical aspects – site security, loading speed, mobile optimization.
- Content signals – depth of topic coverage, alignment with search intent, and text quality.
Does Schema.org Impact EEAT Checklist or Google Rankings?
Schema markup isn’t a direct ranking factor or E-E-A-T indicator, but it helps Google better understand your content:
- Author Schema links content to specific authors.
- Organization Schema provides structured data about your company.
- Review Schema can demonstrate social proof for products.
- FAQ Schema showcases expertise in addressing common questions.
- HowTo Schema highlights practical experience.
While Schema.org doesn’t guarantee better rankings, it aids Google in accurately assessing your content’s expertise, authority, trust.
Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines
The Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG) is a document Google provides to assessors for evaluating search result quality. Key criteria for achieving high E-E-A-T according to about EEAT in the QRG:
- YMYL sites require the highest level of E-E-A-T and formal author expertise.
- Content must fully satisfy user search intent.
- Websites should clearly indicate who is responsible for the content.
- Transparent company information and contact details are essential.
- Sites must be regularly updated with current information.
- Different topics require varying expertise levels (medical topics need medical education, financial issues require relevant certifications).
- The reputation of the site and its authors plays a critical role.

How Google Assesses Author and Content Expertise
Google evaluates author and content expertise through various signals:
- Author bios – detailed information about education, experience, and publications.
- External publications – articles by the author on other authoritative platforms.
- Professional profiles – presence on LinkedIn, academic profiles, or industry associations.
- Citations – how often the author is referenced by other experts.
- Content depth – how thoroughly the topic is covered, going beyond surface-level insights.
- Technical proficiency – use of industry-specific terminology demonstrating deep understanding.
- Alignment with consensus – consistency with widely accepted industry views.
The Role of Website Authoritativeness and Backlinks in E-E-A-T
A website’s authoritativeness heavily depends on its backlink profile and online mentions. Google views links as “votes of trust” from other sites.
Key aspects of backlinks’ impact on E-E-A-T:
- Quality over quantity – one link from an authoritative industry resource can outweigh dozens from irrelevant sites.
- Relevance of linking domains – links from niche-related sites carry more weight.
- Natural profile – links should appear organic, with varied anchor texts.
- Non-linked mentions – even brand mentions on authoritative sites positively impact E-E-A-T.
- Negative links – associations with low-quality sites can harm your EEAT score.
Strategies for building a strong backlink profile include:
- Guest posting – publishing expert articles on relevant platforms
- Niche edits – inserting links into existing content on relevant sites
- Digital PR – earning mentions in authoritative online media
- HARO links – securing citations as an expert
- Contextual links – naturally embedding links in relevant content
These methods not only boost SEO performance but also enhance overall site authoritativeness. All these services are available at LinkBuilder.com – contact us to create an effective link profile.
Proving Trustworthiness: Facts, Sources, and Citations
Trustworthiness is a cornerstone of expertise, authority, and trust. Google evaluates it through several criteria:
- Factual accuracy – alignment with scientific consensus and verified facts.
- Citation of authoritative sources – links to studies, official data, or recognized experts.
- Transparency – clear separation of facts and opinions, with source attribution.
- Comprehensive coverage – presenting multiple perspectives on controversial topics.
- Relevance – updating content with new data.
- Accurate company details – clear contact information and a transparent privacy policy.
- No manipulation – avoiding exaggerations or false promises.
Practical ways to enhance content trustworthiness:
- Cite primary sources rather than secondary interpretations
- Reference peer-reviewed studies
- Include statistics with sources and dates
- Display publication and update dates
- Maintain a clear error-correction policy
- Highlight authors’ qualifications
E-E-A-T and AI-Generated Content: Striking the Balance

Can AI-Generated Content Comply with E-E-A-T?
Using AI to create content doesn’t preclude meeting EEAT checklist standards, but it requires a thoughtful approach:
- AI as a tool, not a replacement. Google doesn’t ban AI-assisted content creation, but entirely generated content without human input may fail to meet E-E-A-T criteria, particularly in terms of experience.
- Human input is critical. An expert must review, refine, and enhance AI-generated content, adding personal experience and unique insights.
- Focus on added value. AI can help structure basic information, but actual value comes from human expertise and experience.
AI can be used for topic research, content structuring, and drafting initial versions. For instance, tools like AI Ranker can analyze popular search queries related to your site’s topic to create a content plan or article structure.
The text should then be significantly reworked by an expert, incorporating their personal experience. AI can also enhance and expand human-created content.
Risks of Fully Automated Content in 2025
Risks of relying solely on automated content include:
- AI detection algorithms. Google is improving its ability to identify content generated exclusively by AI without significant human editing.
- Lack of real experience. AI cannot have firsthand experience – it relies on training data, conflicting with the “Experience” component of E-E-A-T.
- Data relevance issues. AI models are trained on historical data and may include outdated information.
- Uniformity and templated content. Pure AI content follows predictable patterns, detectable by both algorithms and users.
- Loss of audience trust. As users become more aware of AI technologies, they may distrust sites with clearly automated content.
- Authorship and accountability issues. It’s unclear who is responsible for the accuracy of fully AI-generated content, undermining trustworthiness.
How to Refine AI-Generated Content for E-E-A-T Standards
To align AI-generated content with Google's helpful content guidelines, it must be significantly refined:
- Incorporate firsthand experience:
- Include personal observations and practical experience with the product or service
- Add unique details only obtainable through real-world practice
- Use original photos or screenshots to illustrate the content
- Enhance the expertise component:
- Include professional insights unavailable in general sources
- Supplement with specialized knowledge
- Add recent data from current studies
- Provide examples from personal practice
- Boost authoritativeness:
- Cite recognized industry experts
- Link to authoritative sources and studies
- Include opinions from other specialists to support key points
- Ensure trustworthiness:
- Verify all facts and figures for accuracy and relevance
- Include links to primary sources
- Specify publication and update dates
- Ensure the content is free of contradictory claims
How to Create Content That Meets E-E-A-T Standards: A Guide for 2025

Choosing Topics: How to Prove Your Expertise
Selecting the right topics is the foundation of EEAT content. It’s not enough to write about what’s popular; you need to focus on areas where you can demonstrate genuine expertise to align with Google EEAT guidelines.
Leverage Your Strengths
The best topics are those where you can share real-world experience. If you have a professional background in a specific field, use it as a competitive edge. Share nuances only you know and provide insights from practical experience to showcase what is EEAT in action.
Define Your Expert Niche
The narrower and more specific your topic, the easier it is to become a recognized expert. Instead of covering a broad field like “marketing,” focus on a niche like “neuromarketing in mobile apps.” Create interconnected content to form topical clusters, strengthening your position in your chosen niche and boosting EEAT in SEO.
Identify Information Gaps
Analyze which questions lack quality answers. The most valuable content often fills these gaps. If other experts avoid complex topics, your in-depth analysis can serve as a key proof point for your expertise, aligning with EEAT SEO principles.
Plan Your Content Strategy
A strong strategy includes content of varying complexity – from beginner to advanced. Mix formats like guides, case studies, analytical reviews, and research to demonstrate the depth of your knowledge and meet EEAT guidelines while addressing diverse audience needs.
Continuously Develop Expertise
Expertise requires constant growth. Stay updated on trends, engage in professional discussions, and conduct your own experiments. The deeper you dive into your topic, the more valuable your content becomes, reinforcing how to create authoritative content for Google.
Examples of topics that highlight expertise:
- Comparative analyses based on personal testing
- In-depth breakdowns of complex case studies from your experience
- Industry forecasts grounded in real-world insights
- Guides featuring unique methodologies you’ve developed
Depth of Research: How Many Sources Are Needed?
The quality of your content depends on the depth of your research. Google EEAT demands more than superficial coverage – it requires thorough analysis and data validation to ensure trustworthiness.
How many sources should you use? There’s no strict rule, but SEO experts from Ahrefs, Semrush, Content Harmony, and editors at major publications (NYT, Healthline, Mayo Clinic, Nerdwallet) recommend the following for EEAT Google compliance:
- YMYL topics (health, finance, safety) – at least 5–7 authoritative sources
- Informational articles – 3–5 diverse sources
- Highly specialized content – at least three niche-specific sources
- Opinion pieces and reviews – rely on personal experience but back key facts with sources
Quality trumps quantity. Three reliable sources are better than ten questionable ones. Prioritize:
- Peer-reviewed studies and publications
- Official data from government or regulatory bodies
- Materials from recognized experts and universities
- Industry reports with transparent methodologies
Incorporate diverse perspectives: academic research, practical case studies, and historical context. Compare local and global data to make your content more objective and align with EEAT SEO standards.
When working with sources:
- Verify relevance (data older than 2 years may be outdated)
- Refer to primary sources, not summaries
- Critically evaluate research methodologies
- Properly format citations and links
If you conduct surveys, experiments, or collect statistics, include them in your content. This not only builds trust but also makes your material unique, enhancing your EEAT audit results.
Content Formats: Guides, Case Studies, Research, Personal Experience
Different formats highlight various aspects of EEAT Google. The optimal strategy is to combine them effectively.
Step-by-Step Guides (How-to)
These are ideal for showcasing practical experience. The more detailed the guide, the better. Include:
- Warnings about potential challenges
- Tips not found in official manuals
- Visual evidence for each step
Case Study Breakdowns
Real-world examples demonstrate how theory applies in practice. A strong case study structure includes:
- The initial situation and problem
- Decisions made and their rationale
- Results (preferably with metrics)
- Conclusions and lessons learned
Research and Analytics
These strengthen expertise through in-depth analysis. Key elements include:
- Clear methodology
- Representative data
- Practical conclusions, not just facts
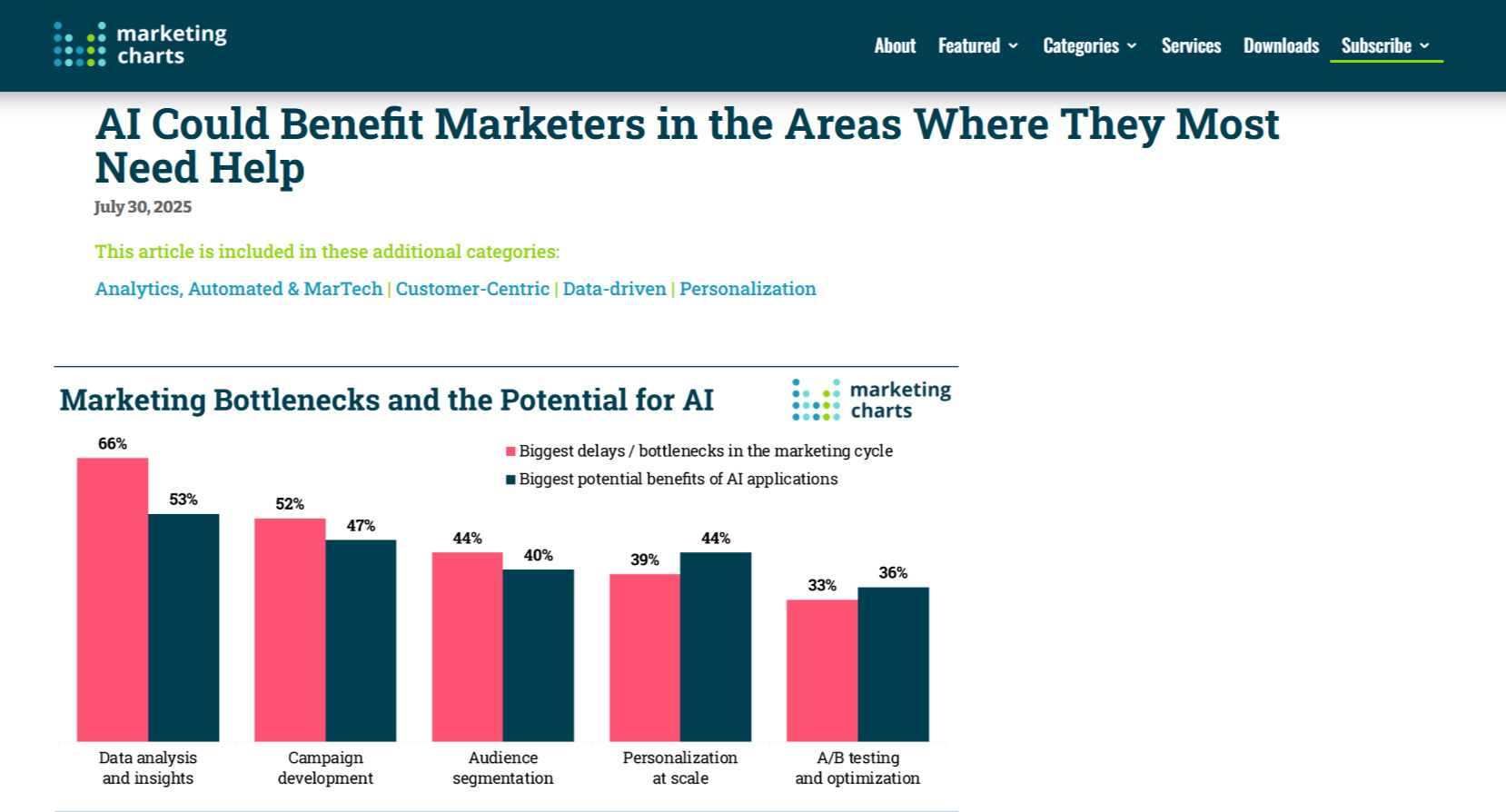
Reviews Based on Personal Experience
These show how a product or method performs in real conditions. Focus on:
- Objective pros and cons
- Non-obvious usage nuances
- Evidence (screenshots, videos, tests)
Expert Interviews
Involving recognized specialists boosts content authority. Ensure:
- Non-generic questions
- Contextualized responses
- Links between theory and practice
How to Showcase Practical Experience in Text
Experience is a core component of EEAT in SEO. To demonstrate it:
- Use the first person. Phrases like “In my experience, this method worked in 80% of cases” or “After a year of testing, I concluded…” immediately signal real-world experience.
- Describe the process, not just the outcome. Readers want to see the journey:
- What challenges did you face?
- How did you overcome them?
- Why did you choose a specific solution?
- Include time markers. References like “After three months of use…” or “In the long term…” make experience tangible.
- Provide specific metrics. Statements like “Conversion increased by 27%” or “Task time was halved” are more compelling than vague claims.
- Share mistakes. Discussing failures and their resolutions builds trust. For example: “I initially tried approach X, but it failed due to Y. Then I adjusted my strategy, and here’s what happened…”
Visual Evidence: Screenshots, Videos, Documents
Text is critical, but visuals amplify trust in EEAT content. The most effective visuals include:
- Annotated screenshots (with arrows or highlights)
- Videos of processes (e.g., testing a tool)
- Graphs from your research
- Certificates, diplomas, or thank-you letters
Use only original materials – no stock images for proof. Ensure visuals are current: screenshots for software or services should reflect the latest version.
Examples of compelling visuals:
- Screenshots of product or service workflows
- Photos of testing results
- Video demonstrations of methodologies
- Graphs showcasing your research findings
- Infographics visualizing collected data
The more you show rather than tell, the higher the audience's trust. For example, LinkBuilder.com’s training guide details how our Guest Post Selection Tool works, using screenshots of the process for clarity.
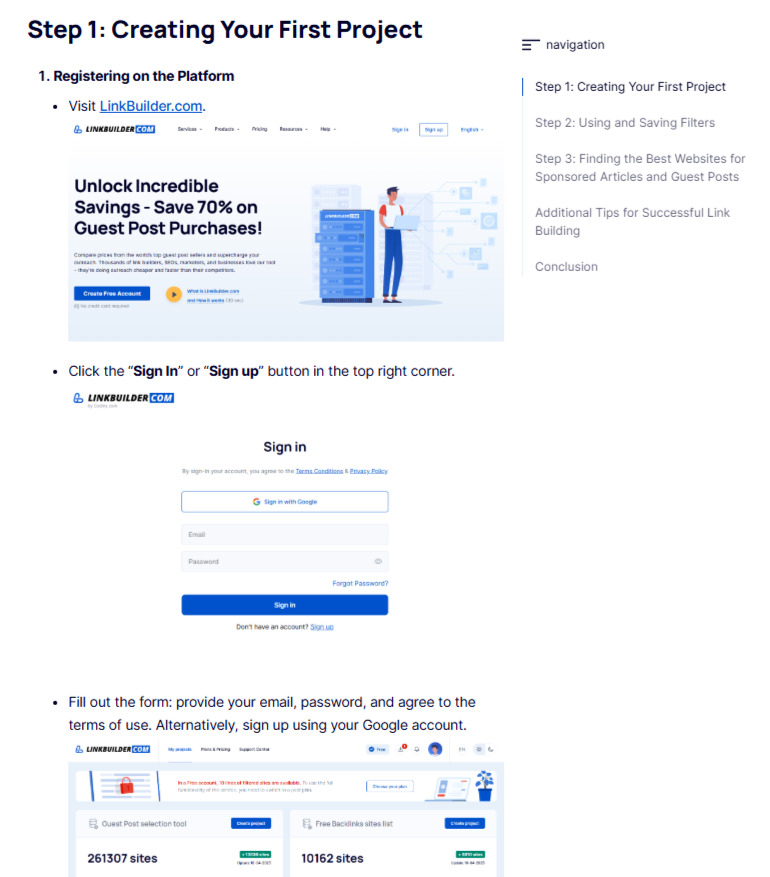
How to Boost Your Site’s E-E-A-T: Technical and Content Methods
Optimizing Author Profiles
Author profiles showcase expertise and authoritativeness, key to how to create authoritative content for Google. An ideal author profile includes:
- A high-quality author photo
- A bio emphasizing relevant experience and education
- A list of professional achievements, publications, or awards
- Details of specialization and areas of expertise
- Membership in professional associations
- Links to professional social media profiles
For example, this is how we format author profiles on LinkBuilder.com’s blog.
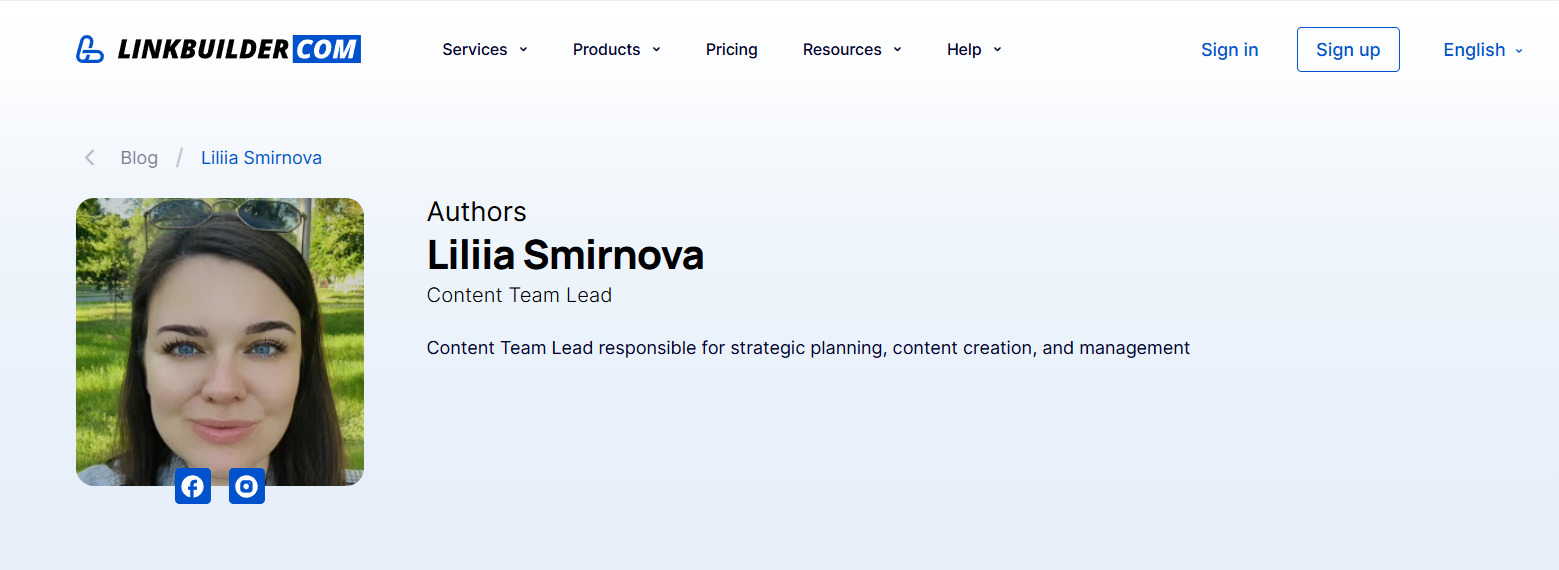
Create a dedicated page for each author with a unique URL and implement Schema Person markup. Ensure every author’s content links to their profile. Consider adding content filtering by author for user convenience.
Enhancing “About Us,” “Contact,” and Team Pages
The “About Us,” “Contact,” and team pages build the foundation for trust in EEAT Google standards. They assure users that your company is real, staffed by actual people, not scammers.
Below are example elements for each page. Not all are mandatory – digital companies may lack a physical office, and startups might not yet have awards. Choose what fits your business.
The “About Us” page could include:
- A detailed company history with key milestones
- A clear mission, vision, and values statement
- Team information highlighting qualifications and experience
- Achievements, awards, publications, or industry event participation
- Client case studies and successful project histories
- Industry partnerships or association memberships
- Details of your business model and work approach
For example, LinkBuilder.com’s About Us page showcases our agency’s strengths and experience with clear metrics.

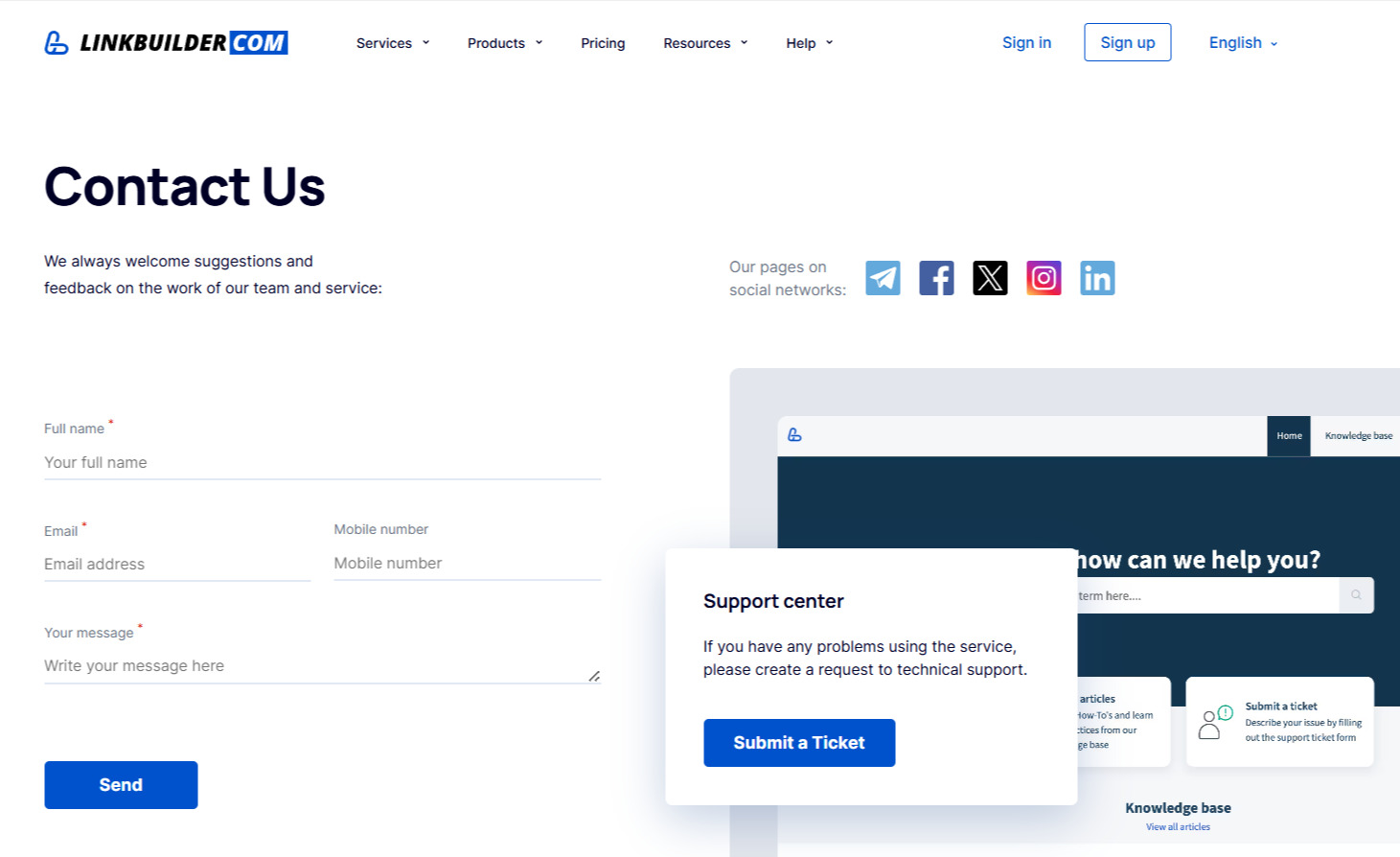
The “Contact” page could include:
- Full contact details: phone, email, social media links
- Office address and a map with location markers
- A user-friendly contact form with clear fields
- Alternative communication channels (messengers, site chat)
For example, LinkBuilder.com’s Contact page includes social media links, a contact form, and a support center link.
For the team page, include:
- Professional photos of key employees
- Detailed profiles with education, experience, and specialization
- Links to LinkedIn or other professional profiles
- Information on publications, speeches, or expertise
- Quotes or personal stories showing passion for their work
- Grouping by department or specialization for larger teams
- Details on company culture and internal values
Additional trust-building elements:
- Client or partner logos (with permission)
- Certificates and accreditations with dates
- Client testimonials with names and companies
- Media mentions with links
- Industry rankings and awards
- Statistics (years in business, client count, successful projects)
- Links to case studies and research
For example, this is how LinkBuilder.com showcases its partners.

Managing Reviews, Recommendations, and Mentions
Client reviews, partner recommendations, and mentions in authoritative sources are powerful signals that boost trust in your brand. They demonstrate real-world experience, confirm expertise, and strengthen industry authority, aligning with Google EEAT guidelines.
System for Handling Client Reviews
Start by automating review collection. Set up triggered emails sent to clients after project completion or purchase. Briefly explain why their feedback matters and make the review process simple.
When displaying reviews on your site, focus on details. Include the reviewer’s name, position, company, and interaction date to enhance credibility. Group reviews by product or service categories to help visitors find relevant feedback.
Use varied formats: text reviews, video interviews, or social media screenshots with publication dates. Add Schema.org/Review markup to improve review display in search results and potentially increase click-through rates.
Managing External Reviews and Reputation
Your website isn’t the only place for reviews. Create and optimize profiles on key industry directories, niche platforms, and services like Trustpilot or G2. Fully complete profiles with logos, current contacts, and service descriptions.
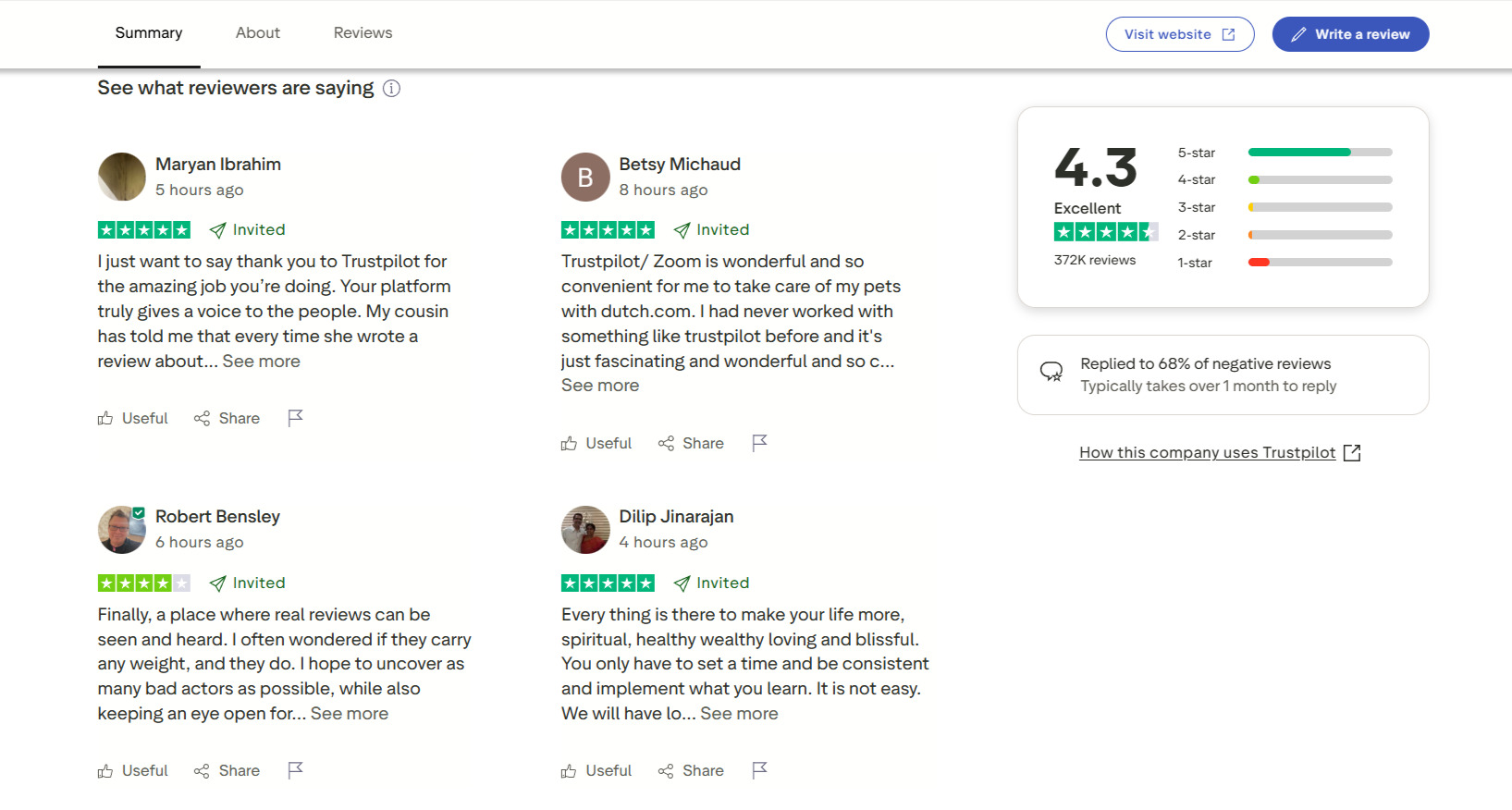
Set up brand mention monitoring to stay informed about new reviews and respond promptly. Pay special attention to addressing negative feedback – professional and constructive responses can enhance trust even in challenging situations.
Working with Recommendations and Expert Endorsements
Personal recommendations from clients and partners are highly valuable. Request written recommendations after successful projects, ideally on company letterhead with the recommender’s signature and contact details.
Create a dedicated section on your site for case studies, including not only project details but also client video testimonials or quotes. Place relevant recommendations on service pages – for example, a client testimonial for a specific service.
Don’t overlook LinkedIn, a platform built for professional recommendations. Encourage satisfied clients to leave endorsements on your profile, especially valuable in B2B where decisions often rely on personal connections and reputation.
Strategy for Managing Media Mentions
Mentions in authoritative publications significantly boost your status with search engines and potential clients. Create a “Media About Us” section on your site to collect these mentions, noting the source, date, and context for each.
Generate newsworthy content – conduct research, publish industry reports, or host events. Build relationships with journalists and bloggers in your niche. Services like HARO (Help a Reporter Out) connect journalists with experts for commentary. You can do this independently or order HARO services from LinkBuilder.com.
Speaking at conferences is another way to earn authoritative mentions. After presenting, publish your talk materials on your site with links to media coverage of the event.
Linking to Authoritative Sources and Research
Linking to authoritative sources is a critical element of EEAT SEO. It shows reliable data back your claims. Always aim for primary sources – scientific studies, official statistics, or regulatory documents.
Prioritize:
- Peer-reviewed academic journals
- Materials from research centers and universities
- Government or regulatory data
- Publications from professional associations
Format links correctly: use descriptive anchor text, set links to open in new tabs (target="_blank"), and add rel="noopener" for security. Mark commercial links with rel="nofollow".
Be transparent – indicate when quoting others’ opinions, provide context about the author and organization. For controversial data, present multiple perspectives with corresponding links to ensure EEAT content credibility.
Keeping Content Fresh
Regular content updates are essential for maintaining high EEAT Google standards. Create a content audit system: catalog all materials, track publication and update dates, and prioritize revisions.
Focus on:
- Statistics and factual data
- Examples and case studies
- Screenshots and visuals
- Tool or service lists
- Methodologies and recommendations
Don’t limit updates to minor edits. Rewrite outdated sections, add new research, and expand with fresh details. Introduce new formats like videos, infographics, or interactive elements.
Inform readers about updates – display the last revision date and add editor’s notes for significant changes. For critical content, maintain a version history.
Fresh, relevant content continues to build expertise and authority, driving consistent traffic and strengthening search rankings over time.
Examples of Sites with High E-E-A-T
Dogster.com

A site about dogs and pet care, covering health, nutrition, training, lifestyle, and breeds.
Dogster stands out by offering expert advice from an international team of veterinarians and dog specialists, helping pet owners access qualified guidance to improve their dogs’ lives.
Why High E-E-A-T?
- Experience: Articles are written by veterinarians, certified trainers, and other dog experts, confirming real-world expertise.
- Expertise: The site covers a wide range of topics – from health to training – demonstrating deep knowledge.
- Authoritativeness: Dogster is a leading resource for dog owners, frequently cited by other authoritative sources.
- Trustworthiness: Content is vetted by veterinarians, with author bios and links to additional resources.
Healthline.com
A health-focused site offering diverse content to help people manage their well-being. It includes information on diseases, treatments, health tips, prevention, and healthy living.
Why High E-E-A-T?
- Experience: Articles are created by individuals with medical education or personal health experiences (e.g., patients with chronic conditions).
- Expertise: Content is reviewed by medical professionals, with a clear editorial policy.
- Authoritativeness: Healthline is cited in media (Forbes, The New York Times) and attracts 150 million monthly visitors.
- Trustworthiness: The site provides contact details and funding transparency.
Consumer Reports
A platform offering advice and recommendations for choosing products and services, with ratings and reviews for categories like cars, appliances, and electronics.
Consumer Reports stands out for its independent evaluations based on expert testing, helping consumers make informed purchasing decisions.
Why High E-E-A-T?
- Experience: Reviews are based on extensive testing, not first impressions.
- Expertise: Independent product testing (from cars to gadgets).
- Authoritativeness: 89 years in operation with a strict editorial policy.
- Trustworthiness: No paid ads, funded solely by subscribers.
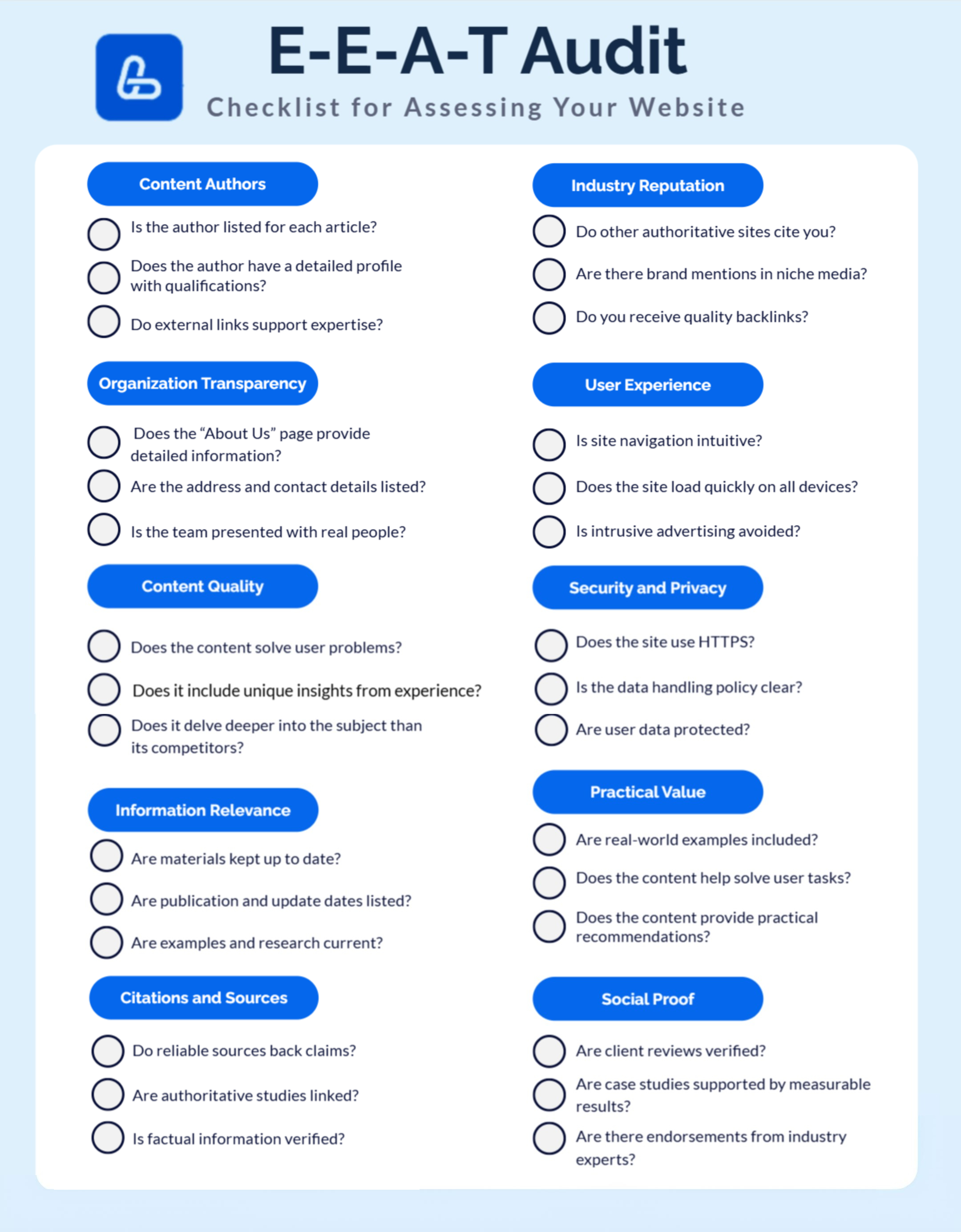
E-E-A-T Audit: Checklist for Assessing Your Website
Regularly conducting an EEAT audit helps identify weaknesses and prioritize improvements. Here’s a step-by-step EEAT checklist for self-assessment.
10 Key Areas for Self-Checking
- Content Authors:
- Is the author listed for each article?
- Does the author have a detailed profile with qualifications?
- Do external links support expertise?
- Organization Transparency:
- Does the “About Us” page provide detailed information?
- Are the address and contact details listed?
- Is the team presented with real people?
- Content Quality:
- Does the content solve user problems?
- Does it include unique insights from experience?
- Does it delve deeper into the subject than its competitors?
- Information Relevance:
- Are materials kept up to date?
- Are publication and update dates listed?
- Are examples and research current?
- Citations and Sources:
- Do reliable sources back claims?
- Are authoritative studies linked?
- Is factual information verified?
- Industry Reputation:
- Are you cited by other authoritative sites?
- Are there brand mentions in niche media?
- Do you receive quality backlinks?
- User Experience:
- Is site navigation intuitive?
- Does the site load quickly on all devices?
- Is intrusive advertising avoided?
- Security and Privacy:
- Does the site use HTTPS?
- Is the data handling policy clear?
- Are user data protected?
- Practical Value:
- Does the content provide practical recommendations?
- Are real-world examples included?
- Does the content help solve user tasks?
- Social Proof:
- Are client reviews verified?
- Are case studies supported by measurable results?
- Are there endorsements from industry experts?
All questions are compiled in a single checklist – save the picture and make use of it.
Tools for Analyzing E-E-A-T
While no tool directly measures E-E-A-T, you can use a combination of services to assess individual components:
Google Search Console:
- Monitor queries Google ranks you for
- Analyze changes after Core Updates
- Track traffic drops and gains
Semrush:
- Analyze backlink profile (quality and relevance)
- Compare visibility with competitors
- Monitor brand mentions
Ahrefs:
- Assess backlink quality
- Track keyword rankings
- Evaluate domain rating
BuzzSumo:
- Track brand and author mentions
- Analyze user engagement
- Assess content virality
PageSpeed Insights:
- Evaluate technical site performance
- Analyze Core Web Vitals
- Identify loading issues
Brand24:
- Monitor online brand mentions
- Analyze mention sentiment
- Track reviews and discussions
How to Address Weaknesses?
After conducting an EEAT audit, you may identify issues. Here’s a step-by-step plan to fix them.
Expertise Issues:
- Engage experts to create or review content
- Create or enhance author profiles
- Add bios with verified qualifications
- Enrich content with unique insights from experience
Authoritativeness Gaps:
- Implement a quality link-building strategy
- Secure mentions in niche media via Digital PR
- Publish guest posts on authoritative platforms
- Participate in industry events as experts
- Launch industry research for citations
Trustworthiness Problems:
- Reverify all facts and data
- Add links to authoritative sources
- Update outdated information
- Enhance site technical security
- Clarify privacy policies
Lack of Demonstrated Experience:
- Include practical examples
- Add screenshots/photos from real projects
- Incorporate personal observations
- Create detailed case studies
- Record video demonstrations of your work
E-E-A-T and Content Marketing in 2025: Trends and Predictions

The EEAT guidelines continue to define quality content, but approaches to implementing them are evolving. Let’s explore key changes shaping content strategies in the coming years.
Personalized Content as the New Quality Standard
Google’s algorithms now assess not only factual accuracy but also content personalization. This reflects a shift in user behavior – people expect solutions tailored to their specific situations, not generic advice.
Deep personalization is now a competitive advantage. Content addressing diverse audience segments shows higher engagement and ranks better in search results.
Algorithms can now distinguish superficial segmentation from meaningful personalization.
To adapt content to new requirements:
- Create materials for different stages of the customer journey
- Develop interactive tools (calculators, diagnostic tests)
- Use dynamic content that adjusts to user parameters
- Implement recommendation systems based on user behavior
Multimedia as Proof of Expertise
Text is no longer the sole way to demonstrate EEAT in SEO. Videos, podcasts, and interactive formats are becoming full-fledged carriers of expertise, offering new ways to prove author competence.
For example, video content:
- Visually demonstrates practical experience
- Shows behind-the-scenes processes
- Adds a human touch to your brand
- Increases engagement and time on site
Podcasts enable expertise through live discussions with invited specialists. Interactive content lets users apply knowledge to their context, boosting interaction time.
How Brands Can Adapt to E-E-A-T
E-E-A-T changes require brands to rethink content creation. The focus is on building an ecosystem where formats and channels reinforce each other.
Developing internal experts is now a strategic priority. This includes training for public speaking, supporting publications on authoritative platforms, and participation in industry events.
Transparency in processes is critical. Users expect not just conclusions but insight into how they were reached. Sharing research methodologies, discussing limitations, and acknowledging potential errors build trust in EEAT content.
Key Adaptation Principles:
- Build a content ecosystem:
- Integrate multiple formats and channels
- Create a cohesive expert image
- Develop topical clusters
- Ensure message consistency
- Invest in internal experts:
- Build personal brands for key employees
- Support expert publications on external platforms
- Train teams for public speaking
- Encourage industry event participation
- Embed real experience in content:
- Involve practitioners in content creation
- Document work processes
- Share real case studies with data
- Discuss failures and lessons learned
- Increase audience transparency:
- Disclose research methodologies
- Explain data sources
- Acknowledge conclusion limitations
- Be honest about sponsorships and partnerships
These shifts require rethinking traditional content marketing but open new opportunities for brands investing in genuine expertise.
Common Mistakes and Myths About E-E-A-T

10 Most Common Errors and Misconceptions
“Adding an author name to an article is enough”
Simply listing a name isn’t sufficient. Google looks for proof of author expertise both on-site and externally. A detailed profile with qualifications and external mentions is essential.
“E-E-A-T is only for YMYL niches”
While EEAT Google is critical for finance and health, Google applies these criteria to all sites. The strictness varies based on the potential impact on users’ lives.
“You can skip source citations”
Citing sources is a key trustworthiness signal. Omitting fact verification lowers content credibility, especially for statistics or research.
“AI content is incompatible with E-E-A-T”
AI-generated content can align with EEAT guidelines if reviewed by an expert, enhanced with real experience, and includes unique insights.
“E-E-A-T is another Google algorithm”
E-E-A-T is not an algorithm but a set of principles implemented through multiple algorithmic signals and manual assessor reviews.
“Writing a lot on a topic is enough”
Volume doesn’t equal quality. A 500-word piece with unique experience and expert insights is more valuable than 5,000 words of generic content.
“Multimedia content (videos, podcasts) doesn’t need E-E-A-T”
All content formats are evaluated for E-E-A-T:
- Videos must show real experience
- Podcasts require genuine experts
- Infographics need verified data sources
Google updated its guidelines to include E-E-A-T assessment for multimedia.
“Client reviews don’t matter for E-E-A-T”
Reviews are critical for demonstrating experience and reputation. They confirm your expertise benefits real people.
“Optimizing a site once is enough”
E-E-A-T requires ongoing maintenance. Regular content updates, new reviews, and fresh mentions are essential.
“Technical factors don’t affect E-E-A-T”
Site security, loading speed, and usability impact trust for both users and Google.
How to Avoid Mistakes
To prevent E-E-A-T errors and create content Google loves:
- Conduct regular EEAT audits
- Involve experts in content creation and review
- Focus on solving user problems, not just SEO metrics
- Document author experience and expertise
- Regularly update existing content
- Use reliable sources with proper citations
- Perform fact-checking before publishing
- Partner with LinkBuilder.com for site optimization
Professional help saves time and resources. LinkBuilder.com’s experts will conduct an E-E-A-T audit, identify improvement areas, create SEO-optimized texts, and ensure all components align with Google EEAT guidelines. Contact us to make your site more expert, authoritative, and trustworthy.










